Explore the groundbreaking era of hydrogen cars in our latest blog. Discover how these vehicles, with zero-emission prowess and advanced technology, are reshaping the automotive landscape.
Uncover the pivotal role hydrogen powered cars play in steering transportation towards a greener future in the 21st century. Dive into the sustainability, innovation, and potential these eco-friendly vehicles hold for a cleaner, more environmentally conscious tomorrow.
1.Introduction: Hydrogen Cars Revolutionizing Transportation
Hydrogen Cars , heralded as the latest marvel in sustainable transportation, are garnering significant attention amid the global pursuit of cleaner and more efficient alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
These innovative vehicles operate by utilizing hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. The environmental benefits of hydrogen cars are compelling, as they contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
However, challenges such as infrastructure development, production costs, and energy-intensive hydrogen production methods pose obstacles to widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, the potential impact of hydrogen cars on urban areas is immense. Their zero-emission nature aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable urban mobility, offering a promising solution for cleaner and quieter transportation.
As technological advancements and infrastructure investments progress, hydrogen cars may play a pivotal role in shaping a more environmentally conscious future for the automotive industry.
2.How Hydrogen Cars Work:
These cars utilize cutting-edge fuel cell technology, where hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen to generate electricity powering the vehicle’s electric motor.
Diverging from traditional internal combustion engines, hydrogen cars produce electricity dynamically, emitting solely water vapor as a clean byproduct. This innovative process underscores their zero-emission advantage, positioning hydrogen cars as an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional vehicles.
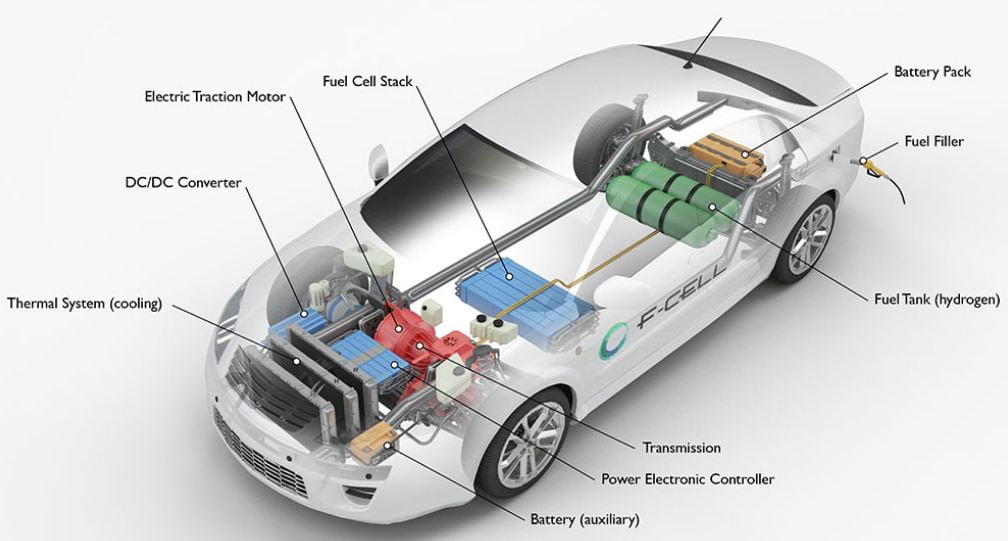
By seamlessly converting hydrogen into electricity with minimal environmental impact, these vehicles represent a promising stride towards sustainable and eco-conscious transportation solutions.
3.Benefits of Hydrogen Cars
These cars offer a multitude of benefits in the pursuit of sustainable transportation. Their foremost advantage lies in environmental friendliness, as these vehicles produce zero emissions during operation, emitting only water vapor.
Hydrogen fuel cell technology provides a rapid refueling experience, comparable to traditional gasoline vehicles, addressing concerns about electric vehicle charging times.
Additionally, hydrogen is a versatile energy carrier, enabling diverse applications beyond transportation, such as industrial processes and energy storage. The abundance of hydrogen resources further enhances its appeal as a clean energy solution.
Furthermore, these cars contribute to reducing dependence on fossil fuels, fostering energy diversity and resilience. As infrastructure and technology continue to advance, the widespread adoption of hydrogen cars holds promise for a greener and more sustainable future.
i) Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology :hydrogen fuel cell vehicles:
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology or hydrogen fuel cell vehicles stands at the forefront of the automotive industry’s pursuit of sustainable and clean energy solutions. Unlike conventional internal combustion engines, hydrogen fuel cells or cell cars generate electricity by combining hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. This innovative technology offers a promising alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, addressing environmental concerns and fostering a more sustainable transportation future.
The process begins with the extraction of hydrogen, usually sourced from water or natural gas. The hydrogen then undergoes a chemical reaction within the fuel cell, producing electricity to power the vehicle’s electric motor. What sets hydrogen fuel cells apart is their efficiency and the speed at which they can be refueled, offering a comparable experience to conventional refueling.
One of the key advantages of hydrogen fuel cell technology is its potential to revolutionize long-range travel. Hydrogen-powered vehicles boast impressive driving ranges and shorter refueling times compared to electric vehicles, making them a compelling option for drivers seeking the convenience of traditional gasoline vehicles without the environmental impact.
As the automotive industry continues to explore sustainable alternatives, hydrogen fuel cell technology emerges as a promising contender, providing a glimpse into a cleaner and greener future for transportation.
Hydrogen Car Infrastructure:
Hydrogen Car Infrastructure plays a pivotal role in shaping the viability and widespread adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles. The development of a robust infrastructure involves the establishment of hydrogen refueling stations, ensuring convenient access for users. While still in its nascent stages compared to traditional fueling stations, the expanding network aims to address the range anxiety associated with hydrogen cars.
Efforts are underway globally to bolster the infrastructure, with an increasing number of refueling stations strategically positioned along major transportation routes. This infrastructure growth is crucial for fostering confidence among hydrogen car users, offering the convenience of refueling similar to traditional gasoline stations. As the network continues to expand, it contributes significantly to the overall sustainability and success of hydrogen cars as a practical and efficient mode of transportation.
4. Pros & Cons of Hydrogen Cars:
- Limited Infrastructure: Scarce availability of hydrogen refueling stations globally inhibits the widespread adoption of hydrogen cars.
- High Production Costs: The expensive nature of hydrogen fuel cell technology poses economic barriers, affecting the affordability of hydrogen-powered vehicles for consumers.
- Energy-Intensive Production: The process of hydrogen production is often energy-intensive and may rely on fossil fuels, raising environmental concerns and partially offsetting the vehicles’ green benefits.
- Environmental Impact: The efficiency of the entire hydrogen supply chain needs improvement to maximize the environmental benefits of these cars, addressing concerns related to their overall ecological footprint.
- Technological Advancements: Continued research and development are necessary to enhance the efficiency and reliability of hydrogen fuel cell technology, ensuring its competitiveness with other sustainable transportation options.
Several automakers have embraced hydrogen technology, with models like the Toyota Mirai, Hyundai Nexo, and Honda Clarity leading the pack. These cars showcase the advancements in design, performance, and safety, making them viable options for eco-conscious consumers.
You may also like: Future Fuels Empowering Change: 6 Positive Paradigms of Redefining the Energy Equation for a Sustainable 21st Century
You may also like: Top Carbon Companies (Stocks, ETFs): Navigating the Green Investment Landscape
You will also like: “Sustainable Futures: The Role of Carbon Credits in Climate Solutions”
You will also like: Carbon Credit for Farmers in India: Nurturing Sustainability and Prosperity
Hydrogen cars present a compelling mix of advantages and challenges. On the positive side, they offer zero-emission driving, addressing environmental concerns by emitting only water vapor. Hydrogen refueling is quick, akin to traditional gasoline, providing a familiar experience for users. Moreover, these vehicles boast extended driving ranges, making them suitable for long-distance travel. However, challenges include the limited infrastructure for hydrogen refueling, hindering widespread adoption. Production of hydrogen often relies on natural gas, compromising its eco-friendly image. The cost of producing and storing hydrogen, coupled with the high price of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, remains a significant drawback. Balancing these pros and cons is vital for users navigating the evolving landscape of sustainable transportation options.
5. Advancements in Hydrogen Technology:
- Advancements in this technology have propelled the viability and appeal of hydrogen as a clean energy source, particularly in the context of transportation. Notable progress includes:
- Efficient Fuel Cells: Ongoing research has led to the development of more efficient and durable fuel cells, improving the overall performance and lifespan of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
- Cost Reduction: Advances in manufacturing processes and materials have contributed to a decline in the production costs of hydrogen fuel cells, making hydrogen technology more economically competitive.
- Green Hydrogen Production: Innovations in electrolysis, particularly using renewable energy sources, have enabled the production of “green hydrogen,” significantly reducing the environmental impact of hydrogen production.
- Infrastructure Expansion: Increasing investments are being made to expand the hydrogen refueling infrastructure, addressing a key limitation and promoting the wider adoption of hydrogen vehicles.
- Integration with Renewables: Improved integration of hydrogen technology with renewable energy sources enhances its role in a broader energy ecosystem, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape.
As these advancements continue, hydrogen technology is poised to play an increasingly crucial role in the transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.
6.Hydrogen Cars vs. Electric Cars:
The competition between hydrogen cars and electric cars represents a key aspect of the evolving landscape of sustainable transportation. Here’s a comparative analysis:

i) Hydrogen Cars:
- Zero Emissions: these cars emit only water vapor, ensuring zero direct emissions during operation.
- Quick Refueling: Hydrogen cars boast rapid refueling times, comparable to traditional gasoline vehicles, offering a convenient user experience.
- Longer Range: these cars often have a longer driving range compared to many electric vehicles, addressing concerns about range anxiety.
- Versatility: these can be utilized beyond transportation, contributing to a versatile energy solution for various industries and applications.
ii) Electric Cars:
- Growing Infrastructure: Electric vehicles (EVs) benefit from a more established charging infrastructure, with a widespread network of charging stations globally.
- Advancing Technology: EV technology has matured rapidly, resulting in increased energy density, longer ranges, and declining costs of batteries.
- Home Charging: Electric cars allow convenient home charging, reducing reliance on external infrastructure for day-to-day charging needs.
- Market Penetration: Electric cars have achieved greater market penetration, with various models available from numerous manufacturers, contributing to consumer familiarity.
iii) Challenges:
- Infrastructure: these cars face challenges in building a robust refueling infrastructure, while electric cars rely on an already expanding charging network.
- Cost: these cars often have higher production and infrastructure costs compared to electric vehicles.
Ultimately, the choice between hydrogen and electric cars depends on factors such as regional infrastructure, driving habits, and environmental considerations, as both technologies contribute to the broader goal of sustainable and low-emission transportation.
7. Government Initiatives and Incentives:
Government initiatives and incentives play a pivotal role in promoting the adoption of sustainable transportation technologies. Measures include tax credits, subsidies, and grants to encourage the production and purchase of environmentally friendly vehicles.
Additionally, investments in research and development, along with the establishment of supportive policies and regulations, aim to create a conducive environment for the growth of clean energy technologies.
These initiatives signal a commitment to reducing carbon emissions, fostering innovation, and accelerating the transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious transportation sector.
8. Environmental Impact Assessment:
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a systematic process that evaluates the potential environmental effects of a proposed project or development.
It involves identifying, predicting, and assessing the environmental impacts, both positive and negative, to inform decision-making. EIA considers various factors such as air and water quality, biodiversity, and social aspects.
The goal is to ensure that development projects are conducted in an environmentally sustainable manner, minimizing adverse effects and promoting responsible resource management. EIA outcomes guide policymakers, developers, and communities to make informed choices that balance developmental needs with environmental preservation.
9. Future of Hydrogen-Powered Vehicles:
Future of Hydrogen-Powered Vehicles holds immense promise as advancements in technology and infrastructure continue to address current challenges. Anticipated developments include:

i) Improved Infrastructure:
Increasing investment in hydrogen refueling infrastructure will mitigate one of the major hurdles to widespread adoption, making cars more accessible.
ii) Technological Refinements:
Ongoing research will likely yield more efficient and cost-effective fuel cell technologies, enhancing the overall performance and affordability of hydrogen vehicles.
iii) Green Hydrogen Production:
The shift towards using renewable energy sources for hydrogen production, known as “green hydrogen,” will reduce the environmental impact, aligning hydrogen cars more closely with sustainability goals.
iv) Market Expansion:
As production costs decrease and consumer awareness grows, the market for hydrogen cars is expected to expand, fostering competition and driving innovation.
Integration with Energy Systems:
These cars may become integral components of broader energy systems, contributing to energy storage, grid balancing, and a more sustainable transportation ecosystem therefore we can see bright Future of Hydrogen-Powered Vehicles.
As these trends unfold, hydrogen cars are poised to play an increasingly prominent role in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable future for the automotive industry.
10.User Experiences & Testimonials:
User experiences and testimonials play a crucial role in shaping perceptions of hydrogen cars. Positive feedback often highlights the smooth and quiet operation, quick refueling times, and the satisfaction of contributing to environmental conservation.
Users appreciate the long driving ranges and the versatility of hydrogen fuel cells. However, challenges such as limited refueling infrastructure and higher initial costs are sometimes noted.
As more individuals share their experiences, these testimonials become valuable in building trust and encouraging others to consider hydrogen cars, contributing to the broader narrative of sustainable and innovative transportation options.
11.Debunking Myths about Hydrogen Cars:
Debunking myths about these cars is essential for a more informed understanding of this emerging technology:
Myth: Inefficient Production:
Contrary to belief, advancements in green hydrogen production methods, utilizing renewable energy, are addressing concerns about the efficiency and environmental impact of hydrogen production.
Myth: Lack of Infrastructure:
While hydrogen refueling infrastructure is not as widespread as electric charging, ongoing developments and investments aim to expand the network, challenging the perception of limited accessibility.
Myth: High Costs:
Technological advancements and increased production efficiency are gradually reducing the costs associated with hydrogen fuel cell technology, challenging the misconception of prohibitively high expenses.
Myth: Safety Concerns:
Hydrogen cars undergo rigorous safety testing, and the fuel itself is no more hazardous than gasoline. Dispelling safety concerns is crucial for fostering public confidence in this innovative technology.
Hydrogen Cars in India: A Roadmap to Sustainable Mobility
Hydrogen cars, a cutting-edge technology in the automotive sector, are gradually making their presence felt in India’s quest for sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solutions. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy alternatives, hydrogen-powered vehicles emerge as a promising option, and their potential impact on India’s transportation landscape is worth exploring.
Current Scenario and Upcoming Hydrogen Cars in India:
While the adoption of hydrogen cars is in its nascent stage in India, there is growing interest and investment in this sector. Major automakers are gearing up to introduce hydrogen-powered vehicles, toyota hydrogen car with several models slated to hit the Indian market in the coming years. The promise of reduced carbon emissions and increased energy efficiency is driving this shift towards hydrogen-based transportation.
Green Hydrogen Cars in India:
Green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy sources, is a key element in making hydrogen cars an environmentally friendly option. Manufacturers are focusing on developing cars that use green hydrogen to address concerns related to sustainability and environmental impact. This approach aligns with India’s commitment to reducing carbon footprints and transitioning towards cleaner energy alternatives.
Safety Considerations and Disadvantages:
One common concern revolves around the safety of hydrogen cars, given the highly flammable nature of hydrogen gas. Manufacturers address this by incorporating advanced safety features and utilizing reinforced tanks designed to withstand impact. However, concerns persist, and educating consumers about safety measures is crucial for wider acceptance.
Despite the promising aspects, hydrogen cars face certain disadvantages, including high production costs, limited infrastructure for refueling, and challenges associated with hydrogen storage and transportation. Overcoming these hurdles is essential for the widespread adoption of hydrogen cars in India.
Advantages of Hydrogen Cars:
- Zero Emissions: Hydrogen cars produce only water vapor as emissions, contributing significantly to reducing air pollution.
- Quick Refueling: Hydrogen cars can be refueled quickly, similar to traditional gasoline vehicles, addressing concerns related to long charging times for electric vehicles.
- Extended Range: Hydrogen cars offer a longer driving range compared to many battery electric vehicles, making them suitable for long-distance travel.
- Versatility: Hydrogen fuel cells can be used in various modes of transportation, including cars, buses, trucks, and even trains, showcasing their versatility.
Timeline for Availability in India:
The timeline for the widespread availability of hydrogen cars in India depends on factors such as technological advancements, infrastructure development, and government initiatives. As automakers continue to invest in research and development, it is anticipated that hydrogen cars will become more accessible to Indian consumers in the next decade.
Types of Hydrogen Cars:
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): These vehicles use fuel cells to convert hydrogen into electricity to power an electric motor.
- Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles (HICEVs): These cars utilize hydrogen in an internal combustion engine, similar to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Hybrid Hydrogen Vehicles: Combining hydrogen fuel cells with conventional internal combustion engines, these vehicles provide flexibility in fuel usage.
In conclusion, the advent of hydrogen cars in India represents a significant stride towards sustainable and eco-friendly transportation. While challenges such as safety concerns and infrastructure development need to be addressed, the potential benefits, including zero emissions and quick refueling, make hydrogen cars an exciting prospect for the future of mobility in India. As technology advances and awareness grows, hydrogen cars may well become a key player in shaping the nation’s transportation landscape.
Toyota Hydrogen Car:
Toyota has been at the forefront of innovation in the automotive industry, notably with its foray into hydrogen-powered vehicles. The company’s commitment to sustainability is exemplified by its hydrogen Toyota models, pioneering a new era in eco-friendly transportation.
Toyota’s hydrogen-powered vehicles, often referred to as fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), are equipped with cutting-edge technology. The Toyota hydrogen engine employs a fuel cell to convert hydrogen gas into electricity, powering the vehicle and emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. These cars, fuelled by hydrogen, exemplify Toyota’s dedication to creating automobiles with reduced environmental impact.
The flagship Toyota hydrogen vehicle showcases the brand’s prowess in engineering and environmental consciousness. The hydrogen-powered Toyota not only offers an emission-free driving experience but also addresses concerns related to electric vehicle charging times. With a focus on efficiency and sustainability, Toyota has positioned itself as a leader in the development of hydrogen cell cars.
While the Toyota hydrogen cell car or hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is a testament to the company’s commitment to green mobility, it’s essential to consider factors like hydrogen car fuel cost. The cost-effectiveness of fueling these vehicles with hydrogen remains a topic of interest and scrutiny within the automotive community. As the automotive landscape continues to evolve, Toyota’s hydrogen-powered cars contribute significantly to the growing market of hydrogen fuel automobiles, driving innovation and sustainability in the industry.
12.Expert Opinions:
Expert opinions on these cars provide valuable insights into the viability and potential of this technology. Many experts acknowledge the environmental benefits of zero-emission hydrogen cars, particularly in addressing climate change.
However, opinions vary on the scalability and competitiveness of hydrogen compared to other clean energy solutions, such as electric vehicles. Some experts emphasize the need for continued investment in research and infrastructure to overcome current challenges.
Others express optimism about hydrogen’s role in sectors beyond transportation, including industrial processes and energy storage. Overall, expert opinions contribute to a nuanced understanding of the opportunities and hurdles in integrating hydrogen cars into the broader landscape of sustainable mobility.
13.Conclusion:
Hydrogen cars epitomize a transformative leap toward sustainable and eco-friendly transportation, holding the promise of reshaping the automotive industry. Their zero-emission advantage, stemming from the clean conversion of hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, distinguishes them as a green alternative.
Notably, these cars boast impressive driving ranges, addressing concerns related to the limited range of some electric vehicles, and advancements in fuel cell technology continue to enhance their overall efficiency.
As urban areas and regions worldwide increasingly pivot towards cleaner energy alternatives, hydrogen cars emerge as a beacon of progress. Their positive environmental impact aligns seamlessly with the global commitment to reducing carbon footprints and combatting climate change.
Moreover, the versatility of hydrogen extends beyond transportation, positioning these vehicles as contributors to broader energy solutions. The potential revolution lies not only in the environmental benefits but also in the transformative effects on the automotive industry.
Hydrogen cars, with their cutting-edge technology, challenge conventional norms and foster innovation. The ongoing development of infrastructure, technological refinements, and a growing emphasis on sustainability collectively indicate that hydrogen cars could indeed spearhead a greener and more sustainable future for transportation on a global scale.

FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1. Are hydrogen cars safe to drive ?
Q2. How does the cost of owning a hydrogen car compare to traditional vehicles?
Q3. What is the availability of hydrogen refueling stations in urban areas?
Q4. Can hydrogen cars be charged at home like electric cars?
Q5.Do hydrogen cars need electricity?
